
The whalesay container is another popular example, let’s instantiate it with our own custom message of ‘YAYYYYY!’ $ sudo docker run docker/whalesay cowsay YAYYYYYY!
CHECK DOCKER SYSLOG FREE
The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent itġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - to your terminal.ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - $ docker run -it ubuntu bashġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - For more examples and ideas, visit: The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs theġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - executable that produces the output you are currently reading.ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - 4. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - 3. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - 2. 1 b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 -ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - Hello from Docker!ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:ġ b2e3f870ddf7 happy_sammet 32295 - 1. Now, if we look at the console of the syslog server we see these stdout lines all converted to syslog messages with priority, timestamp, docker container id, container name, and message. Now let’s check the container id and name (“b2e3f870ddf7” and “happy_sammet”) $ sudo docker ps -aĬONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMESī2e3f870ddf7 hello-world "/hello" About a minute ago Exited (0) About a minute ago happy_sammet

Which shows the typical output to the console where it is invoked. Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID: To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with: The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
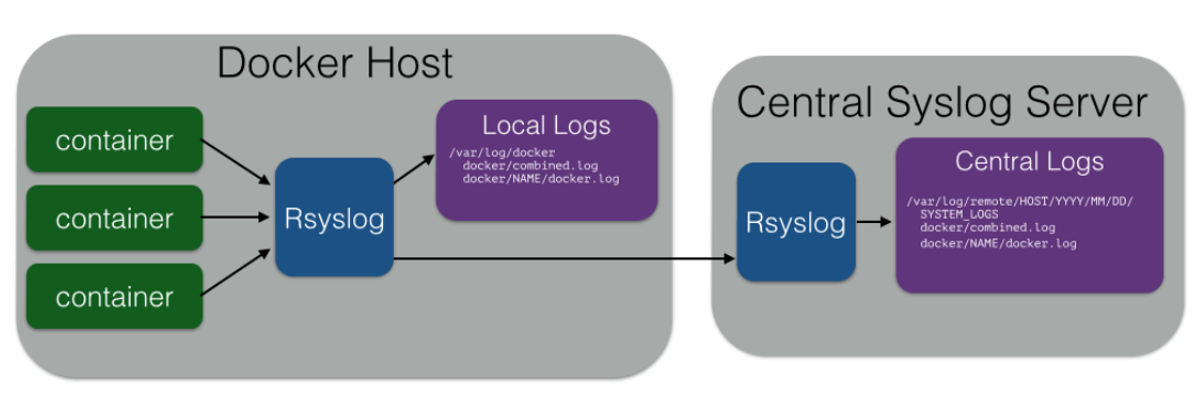
The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs theĮxecutable that produces the output you are currently reading.Ĥ. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.ģ. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.Ģ. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:ġ. This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. Now let’s check if the hello-world container will now send logs through the logspout container, and subsequently to our syslog console. If you need to ignore certain images by name/tag, that is possible usingthe LOGSPOUT and EXCLUDE_LABEL environment variables. volume=/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ $ sudo docker pull gliderlabs/logspout:latest Now we want to start the logspout container, which grabs the logs from all deployed containers and will send all events to our listening syslog server. This proves out our “syslog server” which is where logspout will be output all its messages. Then we run a quick sanity test from another console on the Docker host that sends a message to this TCP server (which happens to be 192.168.1.4 on my system) $ nc -w0 192.168.1.4 514 User Info msg from `hostname` on `date`"Īnd then you will see a message at the pseudo syslog server console: User Info msg from mydockerhost on Mon Apr 17 18:57: And to make it easy, instead of configuring the rsyslog service on our Ubuntu host, we will just use the standard utility netcat to listen on the syslog 514 tcp port and echo any data received.įirst we ensure the rsyslog service is disabled, and start our TCP listener on port 514: $ sudo service rsyslog stop Before moving on, you should be able to run the hello-world container.Īlthough logspout has third-party modules for sending log events to Kafka, Redis, Logstash, and Gelf, the easiest way to illustrate its functionality in this article is to send them to syslog.įor simplicity, we will send the logs to the syslog port of the parent Docker host. If you do not have docker installed yet, see my article here. This is the architectural model of logspout, an open-source project that acts as a router for the stdout/stderr logs of other containers. Docker log collection can be done using various methods, one method that is particularly effective is having a dedicated container whose sole purpose is to automatically sense other deployed containers and aggregate their log events.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
